Product Description
.
ALTERNATOR REGULATOR
When the generator speed changes, the generator regulator adjusts the excitation current of the excitation winding of the engine to keep the generator voltage stable, preventing the generator voltage from being too high and burning the electrical equipment and causing the battery to overcharge, and also prevents The generator voltage is too low, resulting in malfunction of electrical equipment and insufficient battery charging.
| B-Circuit |
| 10.7 – 16.0 Vset |
| BSS(COM) Terminal function |
| With Soft Start and LRC Function |
| With Field Short Circuit Protection |
| BSS or Stator Activated |
| COM ID Code: 20 |
Product production standards
Accord to OEM standard with Source manufacturers raw materials
MOQ Request
Without MOQ request if the items which we have in stock .
2000PCS with customerized box design .
Less than 200PCS with brown box and lable stickers
Lead Time :
30-60Days
Inspection :
100% inspection before packaging in each process
Warranty:
1Year
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2018 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2018 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2018 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2018 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2017 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2017 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2017 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2017 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2016 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2016 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2016 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2016 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 180 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 200 CGI | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 250 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2015 | Petrol Coupe | C 350 | RWD — C204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Diesel Saloon | C 250 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 150KW 204HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 180 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 200 CGI | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 250 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Coupe | C 350 | RWD — C204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 180 | RWD — S204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 180 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 200 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 250 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 350 | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.961 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Estate | C 350 CGI | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.971 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 137KW 186HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 | RWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.921 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2014 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Diesel Saloon | C 250 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 150KW 204HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 180 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 200 CGI | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 250 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Coupe | C 350 | RWD — C204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 180 | RWD — S204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 180 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 200 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 250 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 350 | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.961 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Estate | C 350 CGI | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.971 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 137KW 186HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 | RWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.921 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2013 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Diesel Saloon | C 220 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 125KW 170HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Diesel Saloon | C 250 CDI | RWD — W204 | 2143cc 150KW 204HP OM 651.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 373KW 507HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 63 AMG | RWD — C204 | 6208cc 380KW 517HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 180 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 200 CGI | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 250 | RWD — C204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Coupe | C 350 | RWD — C204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 336KW 457HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 63 AMG | RWD — S204 | 6208cc 358KW 487HP M 156.985 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 180 | RWD — S204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 180 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 200 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 250 CGI | RWD — S204 | 1796cc 150KW 204HP M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 350 | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.961 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Estate | C 350 CGI | RWD — S204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.911 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.948 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 200KW 272HP M 272.971 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 350 4-matic | AWD — W204 | 3498cc 225KW 306HP M 276.957 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1595cc 115KW 156HP M 274.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1597cc 115KW 156HP M 271.910 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 180 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 115KW 156HP M 271.952 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 137KW 186HP M 271.820 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 CGI | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.820;M 271.860 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 200 Kompressor | RWD — W204 | 1796cc 135KW 184HP M 271.950 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 230 | RWD — W204 | 2496cc 150KW 204HP M 272.921 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 280 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2012 | Petrol Saloon | C 300 | RWD — W204 | 2996cc 170KW 231HP M 272.947 |
| Mercedes-Benz | C-Class | 2011 | Diesel Estate | C 220 CDI | RWD — S204 | 2143cc 120KW 163HP OM 651.911 |
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| After-sales Service: | 1 Year Guarantee |
|---|---|
| Warranty: | 1 Year Guarantee |
| Type: | Rectifier |
| Structure: | Brushless Alternator |
| Current Level: | 9(≥90A) |
| Bonding Type of Magnetic Field Winding: | Inner Bonding |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
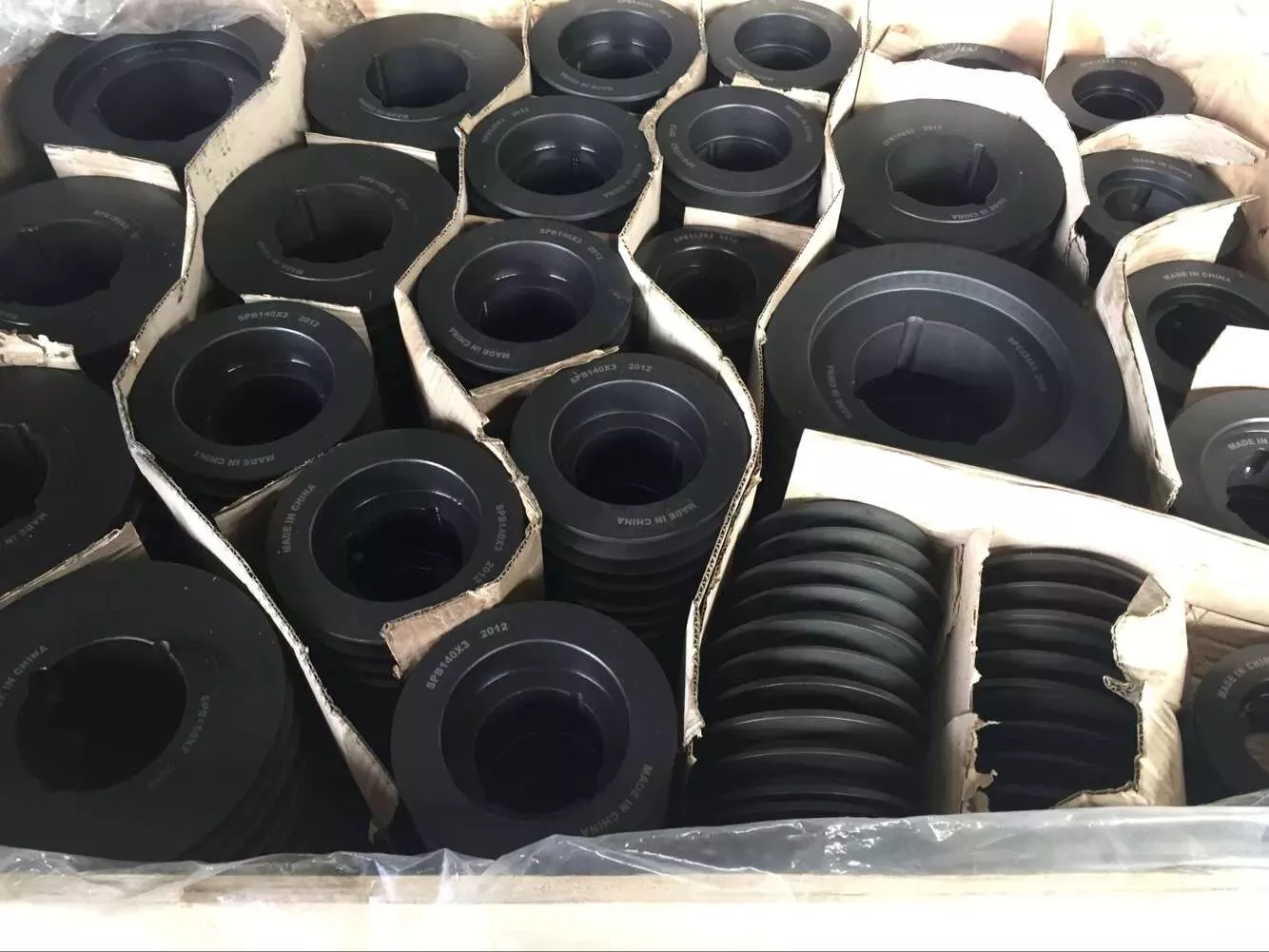

How do pulleys function in various types of vehicles and machinery?
Pulleys play crucial roles in numerous types of vehicles and machinery, enabling the transmission of power, control of mechanical systems, and efficient operation. Here’s how pulleys function in various applications:
1. Automotive Engines: In vehicles, pulleys are commonly used in the engine’s accessory drive system. The crankshaft pulley, also known as the harmonic balancer, is connected to the engine’s crankshaft and drives various accessories such as the alternator, power steering pump, and air conditioning compressor. The pulleys enable the transfer of rotational power from the engine to these accessories, allowing them to perform their respective functions.
2. Belt-Driven Systems: Pulleys are extensively used in belt-driven systems across various machinery and equipment. These systems utilize belts, such as V-belts or timing belts, which wrap around pulleys to transfer power. Examples include conveyor systems, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, and HVAC systems. The pulleys provide the necessary grip and tension to ensure efficient power transmission and drive system operation.
3. Cranes and Hoists: Pulleys are integral components of cranes and hoists, enabling the lifting and movement of heavy loads. Multiple pulleys, often arranged in a block and tackle configuration, are used to create mechanical advantage, reducing the effort required to lift the load. By distributing the load’s weight over multiple strands of rope or cable, pulleys allow for controlled lifting and precise positioning of objects.
4. Construction Equipment: Pulleys are found in various types of construction machinery. For example, in excavators and cranes, pulleys are used in the wire rope systems for lifting and lowering the boom, bucket, or other attachments. Pulleys help in managing the forces involved in these operations, providing smooth and controlled movement.
5. Elevators: Pulleys are essential components in elevator systems. Elevator cars are suspended by steel cables that run over pulleys. These pulleys are connected to an electric motor through a system of gears and sheaves. As the motor rotates the pulleys, the elevator car moves up or down. Pulleys in elevator systems help in efficiently transferring power and maintaining the stability and safety of vertical transportation.
6. Exercise Equipment: Pulleys are widely used in exercise machines and gym equipment to provide resistance and enable adjustable resistance levels. By incorporating pulley systems with different configurations and cable arrangements, exercise equipment can offer a variety of exercises targeting specific muscle groups.
7. Marine Applications: Pulleys are utilized in various marine applications, such as sailboats and winches. Pulleys help in controlling the movement and tension of ropes and cables, enabling sail adjustments, mast raising and lowering, and other rigging operations.
8. Garage Doors: Pulleys are employed in garage door mechanisms to facilitate the smooth opening and closing of the doors. They are used in conjunction with cables or belts, allowing for the transfer of force from the door opener to the door itself.
These examples demonstrate the versatility and importance of pulleys in a wide range of vehicles and machinery. By utilizing pulleys, these systems can achieve efficient power transmission, mechanical advantage, controlled movement, and improved functionality.
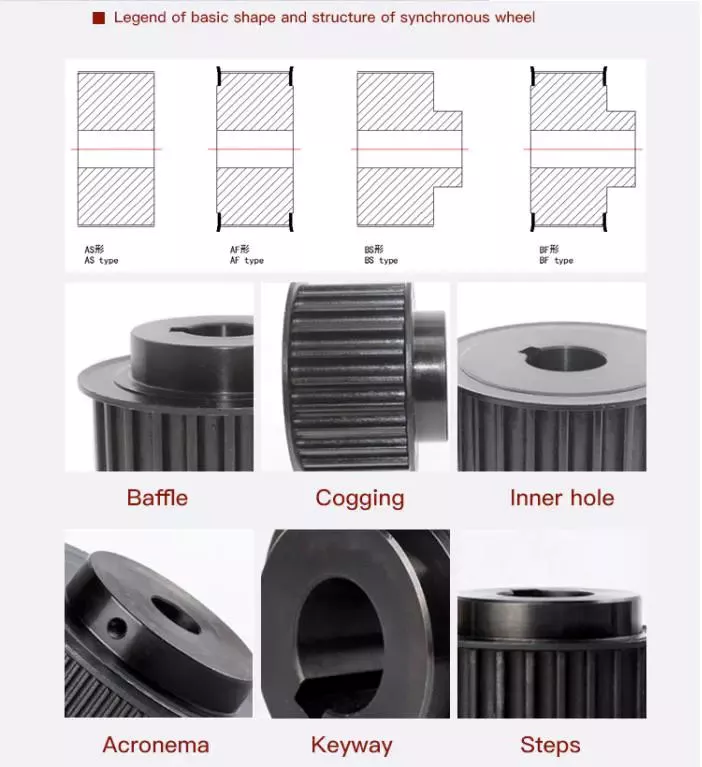
What is the role of pulleys in the mining and construction industries?
Pulleys play a vital role in the mining and construction industries, where they are utilized in various applications to facilitate heavy-duty operations, enhance safety, and improve efficiency. Here’s an overview of the role of pulleys in these industries:
1. Conveyor Systems:
In mining and construction, conveyor systems are extensively used to transport bulk materials, such as ores, rocks, gravel, and construction aggregates. Pulleys are integral components of conveyor systems, guiding and supporting the conveyor belts or chains. They help in maintaining tension, reducing friction, and ensuring smooth movement of materials over long distances. The pulleys used in these systems are designed to withstand high loads and harsh environmental conditions.
2. Hoisting and Lifting Equipment:
Pulleys are crucial in hoisting and lifting equipment used in mining and construction activities. Cranes, winches, and lifting systems often incorporate pulley arrangements to provide mechanical advantage and control the movement of heavy loads. The pulleys, along with ropes, cables, or chains, allow for safe and efficient lifting, lowering, and positioning of equipment, materials, and structures at construction sites or in mining operations.
3. Wire Rope Systems:
In mining and construction, wire ropes are extensively used for various applications, including hauling, towing, and lifting heavy loads. Pulleys, known as sheaves, are employed in wire rope systems to guide and redirect the wire ropes. The sheaves help in maintaining proper alignment, reducing wear, and ensuring efficient power transmission. They are commonly used in applications such as cranes, elevators, and wire rope hoists.
4. Crushing and Screening Equipment:
In the mining and construction industries, pulleys are used in crushing and screening equipment. For example, in crushers, pulleys are utilized to drive the rotating motion of the crusher’s jaws or cones, enabling the crushing of large rocks or ores into smaller sizes. Pulleys also play a role in vibrating screens, helping to generate the necessary vibrations that separate and classify materials based on size.
5. Earthmoving and Excavation Equipment:
Pulleys are incorporated into earthmoving and excavation equipment in mining and construction applications. For instance, in excavators or dragline machines, pulleys are used in the cable systems that control the movement of the bucket or shovel. The pulleys help in extending or retracting the cables, allowing for efficient excavation, loading, and material handling.
6. Tensioning and Alignment:
In mining and construction operations, pulleys are utilized for tensioning and alignment purposes. Tensioning pulleys ensure proper tensioning of belts, ropes, or cables, optimizing power transmission and preventing slippage. Alignment pulleys are employed to maintain the correct alignment of belts or chains, reducing wear, minimizing vibrations, and extending the lifespan of the components.
In summary, pulleys play a critical role in the mining and construction industries, contributing to material handling, lifting and hoisting operations, wire rope systems, crushing and screening equipment, earthmoving and excavation machinery, and tensioning and alignment applications. Their use enhances safety, improves efficiency, and enables the execution of heavy-duty tasks in these demanding industries.

What is a pulley, and how does it function in mechanical systems?
A pulley is a simple machine consisting of a grooved wheel and a rope, cable, or belt that runs along the groove. It is used to transmit force and motion in mechanical systems. Here’s a detailed explanation of how a pulley functions:
1. Mechanical Advantage: The primary function of a pulley is to provide mechanical advantage. By changing the direction of the force applied and distributing it over multiple segments of the rope or belt, a pulley system allows for easier lifting or moving of heavy loads. The mechanical advantage gained depends on the number of pulleys used in the system.
2. Force Transmission: When a force is applied to one end of the rope or belt, it creates tension that causes the pulley to rotate. As the pulley turns, the force is transmitted to the load attached to the other end of the rope or belt. This force transmission allows for the movement and manipulation of objects in mechanical systems.
3. Directional Change: One of the key functions of a pulley is to change the direction of the applied force. By redirecting the force along a different path, a pulley system enables the operator to exert force from a more convenient or advantageous position. This directional change is particularly useful in situations where the force needs to be applied vertically, horizontally, or at an angle.
4. Speed and Torque Conversion: In addition to changing the direction of force, pulleys can also be used to convert speed and torque in mechanical systems. By varying the size of the pulleys or using pulleys of different diameters, the rotational speed and torque can be adjusted according to the requirements of the system. This speed and torque conversion allows for the optimization of power transmission and the matching of different rotational speeds between input and output components.
5. Multiple Pulley Systems: Pulleys can be combined in systems to achieve increased mechanical advantage or to create complex motion patterns. In systems with multiple pulleys, such as block and tackle arrangements, the load is distributed over several segments of rope or belt, further reducing the effort required to lift heavy objects. These systems are often used in cranes, elevators, and other applications where heavy lifting is necessary.
6. Fixed and Movable Pulleys: Pulleys can be categorized as fixed or movable. A fixed pulley is attached to a stationary structure, and its main function is to change the direction of force. A movable pulley, on the other hand, is attached to the load being moved and moves with it. Movable pulleys provide mechanical advantage by reducing the effort required to lift the load.
7. Belt and Rope Pulleys: Pulleys can have different designs depending on the application. Belt pulleys typically have a grooved surface to grip and guide belts, while rope pulleys have a smooth surface to minimize friction and prevent rope wear. The choice between belt and rope pulleys depends on factors such as load requirements, operational environment, and desired efficiency.
Overall, a pulley is a versatile mechanical device that functions as a force multiplier, directional changer, and speed/torque converter in mechanical systems. Its ability to provide mechanical advantage, change force direction, and facilitate complex motion patterns makes it an essential component in various applications, including lifting, transportation, and power transmission.


editor by CX
2024-05-09
